48uep6bbphidvals|695
48uep6bbph|2000F98CTab_Articles|Fulltext
Gastroesophageal reflux disease is a common problem seen in the course of duodenal ulcer treatment.Although an increase in BMI during this therapy is claimed to play a major role in the development of reflux disease, the cause of BMI gain remains obscure.[1] Patients with duodenal ulcer commonly suffer from hunger pain. So they tend to eat more to relieve the pain, leading to BMI increase. Herein, the idea worth researching is the impact of impulsive eating habit of the patients with duodenal ulcer on the increase of BMI and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
The health expenses for increased BMI related disorders like gastroesophageal reflux disease makes such research pertinent. We wish to emphasize that impulsive eating is frequently seen in due course of a duodenal ulcer, because patients state that it helps relieve the symptoms of ulcer. In this regard, we examined the BMI of 105 consecutive dyspepsia patients with and without a duodenal ulcer presenting in our outpatient clinic.
We observed a statistically significant difference in the BMI of dyspepsia patients with and without a duodenal ulcer (p<0.05) (Table 1).
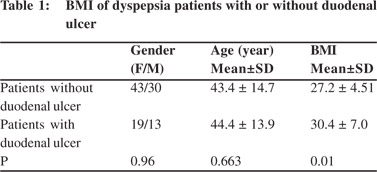 Recent data demonstrates the association between impulsive eating habits and BMI.studies suggests that early monitoring of food addiction symptoms may help reduce the establishment of compulsive food consumption patterns which lead to weight gain and obesity.[2] Our preliminary data highlights that impulsive eating habits can play a considerable role in BMI increase in dyspeptic patients. Therefore, assessment of food consumption patterns is important to prevent BMI increase and associated reflux disease. Accordingly, this issue is worth investigating in patients with duodenal ulcer. And further studies are necessary to clarify this association.
References
Recent data demonstrates the association between impulsive eating habits and BMI.studies suggests that early monitoring of food addiction symptoms may help reduce the establishment of compulsive food consumption patterns which lead to weight gain and obesity.[2] Our preliminary data highlights that impulsive eating habits can play a considerable role in BMI increase in dyspeptic patients. Therefore, assessment of food consumption patterns is important to prevent BMI increase and associated reflux disease. Accordingly, this issue is worth investigating in patients with duodenal ulcer. And further studies are necessary to clarify this association.
References
- Yang YJ, Sheu BS, Chang WL, Cheng HC, Yang HB. Increased body mass index after H. pylori eradication for duodenal ulcer predisposes to erosive reflux esophagitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43:705–10.
- Murphy CM, Stojek MK, MacKillop J. Interrelationships among impulsive personality traits, food addiction, and Body Mass Index. Appetite. 2014;73:45–50.