48uep6bbphidcol2|ID
48uep6bbphidvals|3011
48uep6bbph|2000F98CTab_Articles|Fulltext
IBS is the commonest variety of Functional Abdominal Pain Disorder (FAPD). As per the currently recommended ROME IV diagnostic criteria, it is defined by the presence of abdominal pain at least 4 days per month (for minimum 2 months) related to defecation and associated with the change in frequency and consistency of stool. The ROME IV recommendations provide a symptom based diagnostic tool for FAPD and IBS1.
Interleukin-6 (IL6) is a cytokine protein that has got a pro inflammatory role and plays a significant part in maintaining immune homeostasis in the body. The IL-6 gene, located on the short arm of human chromosome 7 (7p21), presents several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). One of the later is localized in the promoter region (-174 G/C) and is associated with the variations in quantity and expression of IL-6. These variations have been implicated in the disease modulation in many chronic inflammatory and neoplastic disorders. Though the exact pathophysiology of IBS is yet to be ascertained, a major role of inflammation has often been suggested. Previous reports have also noticed that SNP of IL-6 promoter may influence the disease activity in IBS.
Case Report
11 years old twins (sister and brother) were referred to gastroenterology clinic with recurrent peri-umbilical pain 3-4 times in a week for the last 6 months. The pain was associated with alteration of bowel habits with alternating diarrhea and constipation. They both had episodic pains lasting between 15-30 minutes each time. They were born following in vitro fertilization and were dizygotic twins born to non-consanguineous parents. Their current BMIs were above 50th centile. There was no significant past history apart from intermittent wheeze for which they were intermittently using salbutamol inhalers. They were up to date with their immunization and their developmental milestones were all normal. There was no significant family history of gastrointestinal disorders. Following the principles of ROME IV diagnostic criteria, they were diagnosed to be suffering from IBS, based on the history and clinical progression. Before referral they had normal CT scans of abdomen as well as normal upper and lower GI endoscopies. Subsequent investigations were performed following the unit protocol.
At the time of initial diagnosis, the IBS Symptom Severity Score (IBS-SSS)2 was 200 for the brother and 250 for the sister, both signifying moderate diseases severities. Their Coeliac screening including the Anti tissue Trans glutaminase IgA antibodies were negative. Other results (Table 1) had revealed normal hemoglobin and blood counts with marginally raised ESR and C Reactive Proteins. The serum Vitamin D was significantly low and the serum IgE levels were markedly raised. The fecal calprotectin levels were marginally elevated and the serum Interleukin-6 levels (by electro chemo luminescent assay) were significantly high.
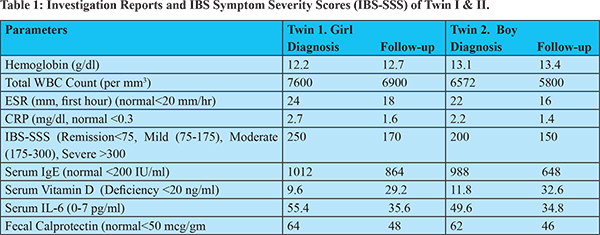
Since the serum Vitamin D levels were significantly low (<20 nanogram/ml), they were given oral Vitamin D supplements of 60000IU weekly for 6 weeks. Follow-up after 6 months from the initial diagnoses revealed marginal improvements in the IBS-SSS (from moderate to mild severity), along with marginal decrease in the levels of serum IgE, Interleukin-6 and fecal Calprotectin levels (Table 1).
Genetic studies performed using Polymerase Chain Reaction- Sequence Specific Primer (PCR-SSP) amplification of the target sequence had revealed SNPs of IL-6 Promoters (-174 G/C) in both siblings.
Discussion
In these twins, following the diagnosis, the diets were modified to eliminate Fermentable oligo-, di- and mono-saccharides carbohydrates and polyols (FODMAPs), as these were identified to aggravate the symptoms. Previous studies with twins have suggested that there is a higher concordance of occurrence of IBS in monozygotic twins than in dizygotic twins3. A previous report had also concluded that there are polymorphism differences in cytokine genes between patients with IBS and healthy controls with a significant trend as regards to SNP of IL-6 Promoter (-174 G/C)4. They had past history of recurrent wheezing and the serum IgE concentrations were markedly increased. Increased prevalence of allergies and atopic disorders including asthma has been shown in patients with IBS. But the limited research conducted till date with small sample sizes have failed to demonstrate an exact link with immunoglobulin E (IgE)5. Finally, along-with marginal reduction in serum IL-6 and serum IgE levels, the siblings also had a marginal decrease in fecal Calprotectin levels following oral Vitamin D supplementation. Previous reports have suggested that Vitamin D supplementation can be effective in treating adolescents with IBS and vitamin D deficiency with a significant improvement in the IBS-SSS6. However, its effect on fecal Calprotectin level is yet to be ascertained.
Conclusion
Dietary adjustments and oral vitamin D supplementation had resulted in symptomatic improvements in dizygotic twins with IBS and documented vitamin D deficiency, at the time of diagnosis. It had also led to a reduction of serum IgE and the pro inflammatory markers like serum IL-6 and fecal Calprotectin. Finally, the SNP of IL-6 Promoter (-174 G/C) could have explained a significant elevation of serum IL-6 in these siblings, which might have contributed to the severity and progression of their disease process.
References
- Hyams SJ, Lorenzo DC, Saps M et al. Childhood Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders: Child/ Adolescent. Gastroenterology 2016; 150:1456-1468.
- Francis CY, Moris JF, Whorwell PJ. The irritable bowel severity scoring system: A simple method of monitoring irritable bowel syndrome and its progress. Aliment pharmacol Ther. 1997;11: 395–402.
- Levy RL, Jones KR, Whitehead WE, Feld SI, Talley NJ, Corey LA. Irritable bowel syndrome in twins: heredity and social learning both contribute to etiology. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:799–804
- Santhosh S, Dutta AK, Samuel P, Joseph AJ, Kumar A, Kurian G. Cytokine gene polymorphisms in Irritable bowel syndrome in Indian population - A pilot case control study. Tropical Gastroenterology 2010;31(1):30–33
- Petitpierre M, Gumowski P, Girard JP. Irritable bowel syndrome and hypersensitivity to food. Ann Allergy. 1985;54:538–540.
- Doaa El Amrousy, Samir Hassan, Heba El Ashry,1 Mohamed Yousef,1 and Hossam Hodeib. Saudi J Gastroenterolv.24(2); Mar-Apr 2018 PMC590047.