48uep6bbphidcol2|ID
48uep6bbphidvals|1817
48uep6bbph|2000F98CTab_Articles|Fulltext
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is an excellent investigational modality for evaluation of various mediastinal pathologies.1,2 It is perhaps the most sensitive method for the diagnosis of posterior mediastinal lesions and lymph nodes.3 However, complete mediastinal evaluation is not possible with EUS because of its limited ability to visualise the anterior mediastinum because of the presence of the trachea and bronchi anteriorly.
Case Report
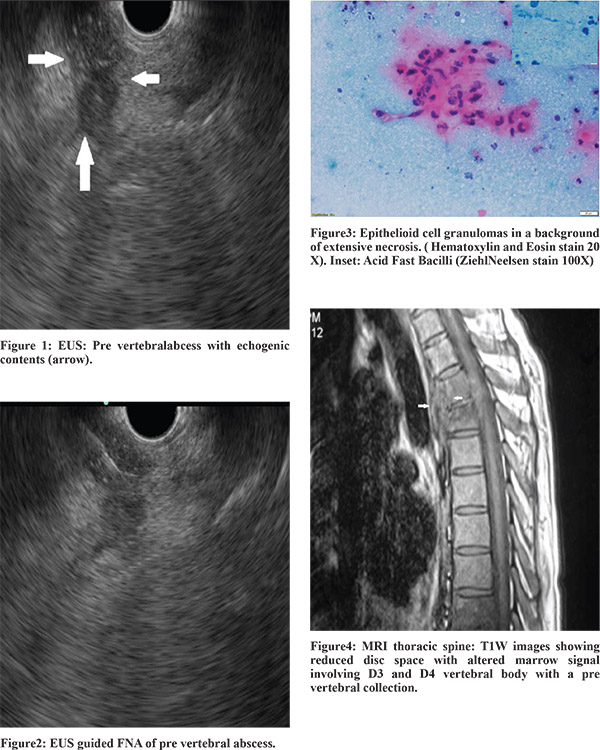
A 38-year old male patient was referred to us for evaluation of ascites of two months’ duration. He had a history of significant alcohol consumption and an ultrasound abdomen revealed ascites along with an enlarged liver with an irregular outline and intra abdominal collaterals. There were no varices on gastroscopy and contrast enhanced computed tomography (CECT) of abdomen revealed findings similar to that of ultrasound. Ascitic fluid analysis revealed a high gradient ascites with a high adenosine deaminase value (108 IU/l) and absence of malignant cells. He was started on diuretics and anti tubercular therapy (ATT). However, he continued to require repeated therapeutic paracentesis. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) was done to look for peritoneal deposits but none could be identified in the upper peritoneum. A few enlarged celiac lymph nodes were identified and fine needle aspiration (FNA) cytology revealed reactive lymphoid hyperplasia. No significantly enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes were seen but a small pre vertebral abscess was identified in the upper mediastinum (Figure1). An EUS-guided FNA yielded cheesy white material (Figure2) and a cytological examination revealed epithelioid cell granulomas in a background of extensive necrosiswith the presence of acid fast bacilli (Figure3). Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the thoracic spine revealed an altered marrow signal involving the body of the third and fourth thoracic vertebra with a pre-vertebral collection showing heterogeneous enhancement on contrast (Figure4). He was continued on ATT and diuretics and did not require further paracentesis after completion of three weeks of treatment.
Discussion
EUS FNA is an excellent diagnostic modality for the evaluation of posterior mediastinal lymph nodes as well as soft tissue lesions.1-3 Various studies have demonstrated the safety and efficacy of EUS FNA in these diseases. Diseases involving the anterior vertebral space and vertebrae in the mediastinum can be potentially diagnosed by EUS because of the close relation of these structures with the esophagus. However, there are only few reports of diagnosis of various vertebral pathologies by EUS. There have been reports of diagnosis of anterior vertebral osteophytes by EUS but the diagnosis of pre-vertebral tubercular abscess by EUS-guided aspiration has not been previously reported.4,5
References
- Larsen SS, Krasnik M, Vilmann P, Jacobsen GK, Pedersen JH, Faurschou Pet al. Endoscopic ultrasound guided biopsy of mediastinal lesions has a major impact on patient management. Thorax. 2002;57:98–103.
- Wildi SM, Hoda RS, Fickling W, Schmulewitz N, Varadarajulu S, Roberts SS, et al. Diagnosis of benign cysts of the mediastinum: the role and risks of EUS and FNA. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58:362–8.
- Vilmann P, Larsen SS. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided biopsy in the chest: little to lose, much to gain. Eur Respir J. 2005;25:400-1.
- Rana SS, Bhasin DK, Rao C, Gupta R, Nagi B, Singh K. Thoracic spine osteophyte causing dysphagia. Endoscopy. 2012;44 Suppl 2 UCTN:E19-20.
- Peter S, Degen L. A spur sign in the EUS evaluation of dysphagia. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008;68:147-8.